Picture this: you’re in need of a shredder to dispose of confidential documents, but you’re not quite sure which one to choose. Fear not, for this article is here to shed some light on the matter. We’ll be exploring the fascinating world of shredders and uncovering the various security classifications they come in. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of the different levels of security these mighty machines offer, equipping you to make an informed decision that will keep your sensitive information safe and sound. Let’s dive in, shall we?
Overview of Shredders
Definition of Shredders
Shredders are mechanical devices used to destroy documents and other materials by cutting them into small pieces or strips. They are commonly employed in offices, homes, and various industries to ensure the security and confidentiality of sensitive information. By rendering the materials unreadable and irretrievable, shredders play a vital role in safeguarding personal, financial, and business data.
Usefulness of Shredders
Shredders serve several important purposes. Firstly, they protect individuals and organizations from the risk of identity theft and fraud. With the increasing prevalence of cybercrime and data breaches, properly disposing of documents containing sensitive information has become crucial. By shredding documents, you can greatly reduce the chances of your personal or business data falling into the wrong hands.
Secondly, shredders contribute to environmental sustainability. Once documents are shredded, the paper can be recycled and reused, minimizing the need for new paper production and reducing the strain on natural resources. This promotes a more eco-friendly approach to document disposal and aligns with the principles of sustainability and conservation.
Types of Shredders
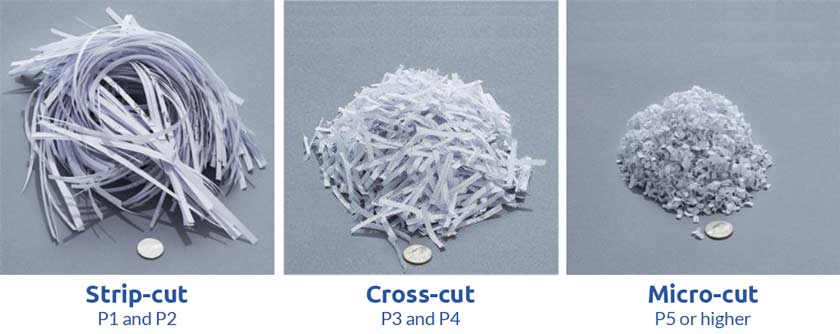
Shredders come in various types, each designed for different levels of security and shredding requirements. The most common types include strip-cut, cross-cut, micro-cut, and high-capacity shredders.
Strip-cut shredders cut documents into long, thin strips, providing a basic level of security suitable for materials without highly confidential information. Cross-cut shredders, on the other hand, create smaller, confetti-like pieces, enhancing security by making it extremely difficult to reconstruct shredded documents.
For heightened security needs, micro-cut shredders are capable of producing tiny particles, rendering the shredded material virtually impossible to reassemble. High-capacity shredders cater to large-scale shredding operations, accommodating a higher volume of documents and offering efficient shredding processes.
Working Mechanism of Shredders
Shredders operate by feeding documents into a slot or opening, where they are pulled through rotating blades or cutting cylinders. These blades or cylinders slice the documents into strips or particles, depending on the type of shredder. The shredded material is then collected in a bin or receptacle for disposal or recycling.
Some advanced shredders feature additional functionalities, such as automatic feeding, jam detection and prevention, and even the ability to shred other materials like CDs or credit cards. The working mechanism of shredders ensures the thorough destruction of documents, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Importance of Security Classification
Definition of Security Classification
Security classification involves categorizing and labeling information or materials according to their level of sensitivity and the extent of protection they require. It allows individuals and organizations to understand the potential risks associated with specific data and implement appropriate security measures. Security classification ensures that only authorized personnel have access to sensitive information, reducing the likelihood of data breaches and unauthorized disclosures.
Security Risks
Without proper security classification, information can be easily compromised, leading to severe consequences. Unauthorized disclosure of confidential data can result in financial loss, damage to reputation, legal liabilities, and the violation of privacy laws. It can also expose organizations to intellectual property theft, competitive disadvantage, and compromise national security interests. Understanding the security risks involved emphasizes the significance of implementing a robust security classification system.
Need for Security Classification in Shredders
Security classification plays a crucial role in shredding processes. Different types of shredders are designed to handle specific security classifications, ensuring that the shredded material meets the required level of protection. By properly classifying documents, you can ensure that they are shredded using the appropriate shredder type, thereby maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information.
Factors Influencing Security Classification
Data Sensitivity
The sensitivity of the data being handled is the foremost factor in determining the security classification. Data that contains personal identifying information, financial details, trade secrets, or confidential business strategies requires higher security measures. Assessing the sensitivity of data helps in selecting the right shredder classification to ensure adequate protection.
Legal Requirements
Legal requirements, such as data protection laws and industry-specific regulations, dictate the level of security classification needed for certain types of information. Compliance with these regulations is essential to avoid legal repercussions and maintain the trust of customers, partners, and stakeholders. Shredders must be chosen in alignment with these legal requirements to maintain compliance.
Industry Standards
Different industries often have specific standards and guidelines regarding the protection and disposal of sensitive information. Healthcare, financial services, and government sectors, for example, have stringent requirements when it comes to data security. Adhering to industry standards ensures that the chosen security classification for shredders meets the necessary criteria for safeguarding data within a specific industry.
Infrastructure and Budget
The capacity and capabilities of a shredder are influenced by the available infrastructure and budget. Assessing the shredding needs, the volume of documents, and the resources at hand helps determine whether a high-capacity shredder or a more basic model is suitable. Finding a balance between the required security classification and the available resources is essential for efficient and cost-effective shredding operations.
Levels of Security Classification
Level 1: General Shredding
Level 1 is the lowest level of security classification, suitable for materials that do not contain confidential or sensitive information. This includes non-sensitive documents, general office waste, or items that require disposal but do not pose any risk if accessed by unauthorized individuals. Strip-cut shredders are commonly used for level 1 shredding.
Level 2: Basic Confidentiality
Level 2 classification is designed for materials that contain basic confidential information. This includes internal documents, routine correspondence, and items that would benefit from a higher level of security than general shredding. Cross-cut shredders are typically used for level 2 shredding.
Level 3: High Confidentiality
Level 3 is an intermediate security classification suitable for materials that contain sensitive information that could cause minor harm if accessed by unauthorized individuals. Examples include financial documents, client records, and proprietary business information. Cross-cut or micro-cut shredders are recommended for level 3 shredding.
Level 4: Very High Confidentiality
Level 4 classification is for materials that contain highly sensitive information that could cause significant harm if accessed by unauthorized individuals. This includes classified documents, intellectual property, and trade secrets. Only micro-cut shredders meet the stringent security requirements of level 4 shredding.
Level 5: Top Secret Shredding
Level 5 is the highest level of security classification, suitable for materials representing top-secret information that, if accessed by unauthorized individuals, could cause extreme damage to national security or critical infrastructure. Usually, specialized devices are employed specifically for top-secret shredding operations.
Classification Criteria for Shredders
Shred Particle Size
The shred particle size produced by a shredder is a critical factor in determining its security classification. Smaller particle sizes make it increasingly difficult to reconstruct shredded documents, enhancing security. Shredders that produce larger particle sizes or long strips are suitable for lower security levels, while shredders that produce fine particles are required for higher security levels.
Cross-Cut vs Strip-Cut Shredding
The choice between cross-cut and strip-cut shredding depends on the desired level of security. Strip-cut shredders produce long strips that are easier to reconstruct compared to cross-cut shredders, which create smaller confetti-like pieces. Cross-cut shredding provides higher security as the shredded material is more difficult to piece together.
Document Capacity and Speed
The document capacity and shredding speed of a shredder should align with the specific needs of an organization. High-capacity shredders are suitable for large volumes of documents, streamlining the shredding process and enhancing productivity. However, smaller shredders with lower capacities may be sufficient for organizations with lower shredding requirements.
Security Features
Shredders may come equipped with security features such as auto-reverse or anti-jam mechanisms to prevent the shredder from jamming or overheating. Other features, like lockable bins and password protection, enhance the security of the shredded material while it awaits disposal. Evaluating the security features of a shredder ensures that it meets the necessary requirements for protecting sensitive information.
Noise Level
The noise level of a shredder can be an important consideration, particularly in office environments where noise reduction and employee comfort are valued. Many shredders now offer quieter operation without compromising performance. Choosing a shredder with an acceptable noise level ensures a conducive working environment.
Maintenance and Upkeep
Assessing the maintenance requirements of a shredder is essential for its long-term performance and durability. Regular cleaning, lubrication, and proper use contribute to the efficient operation and extended lifespan of the shredder. Understanding the maintenance needs and ensuring they align with the available resources helps avoid disruptions and costly repairs.
Understanding Shredder Certifications
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) provides guidelines and standards for secure information destruction. Their certification process ensures that shredders meet specific criteria for secure document destruction. Shredders that have undergone NIST certification give users confidence that their sensitive information will be properly protected.
Conformité Européene (CE)
The Conformité Européene (CE) marking is an indication that a product complies with European Union (EU) legislation regarding health, safety, and environmental protection standards. CE certification for shredders ensures that they meet the necessary safety requirements and can be legally sold and used within the EU.
Defense Security Service (DSS)
The Defense Security Service (DSS) is responsible for assessing and certifying shredders used in U.S. government facilities. The DSS certification process evaluates the effectiveness and reliability of shredders, ensuring they meet the highest security standards for classified document destruction. Shredders certified by the DSS offer enhanced confidence in protecting sensitive government information.
Choosing the Appropriate Security Classification
Assessing Data Sensitivity
Before selecting a security classification for your shredder, it is important to conduct a thorough evaluation of the sensitivity of the data you handle. Consider the potential risks associated with unauthorized access or disclosure and determine the level of protection required based on the nature of the information.
Compliance with Legal and Industry Standards
Ensure that the selected security classification aligns with applicable legal requirements and industry standards. Consider the specific regulations and guidelines that apply to your organization’s sector and ensure that the chosen security classification meets or exceeds the necessary criteria.
Available Infrastructure and Budget
Evaluate the infrastructure and budget available for implementing secure shredding practices. Consider the volume of documents, the number of users, and the resources needed to support the chosen security classification. Finding a balance between the desired security level and the available resources is crucial in selecting the appropriate shredder.
Common Mistakes in Security Classification
Underestimating Data Sensitivity
One common mistake is underestimating the sensitivity of the data being handled. Failing to recognize the potential harm that unauthorized access or disclosure of certain information can cause may lead to inadequate security measures. Properly assessing data sensitivity ensures that the appropriate security classification and corresponding shredder are chosen.
Ignoring Legal and Industry Requirements
Neglecting legal and industry-specific requirements can have severe consequences, including legal liabilities and reputational damage. Failure to comply with data protection laws or industry regulations can result in fines, penalties, and loss of trust. Proactively considering and adhering to these requirements is crucial in maintaining the security and integrity of sensitive information.
Overlooking Infrastructure and Budget Constraints
Overlooking infrastructure and budget constraints can lead to inefficient shredding processes or inadequate security measures. It is important to consider the available resources, such as the capacity of the shredder and the availability of maintenance and support, when selecting the appropriate security classification. Ignoring these limitations may result in increased costs and operational inefficiencies.
Implementing Security Measures
Secure Shredding Policies and Procedures
Developing and implementing secure shredding policies and procedures is essential for maintaining the integrity of sensitive information. Clearly define the steps for handling, shredding, and disposing of different types of documents. Train employees on these policies and ensure they understand the importance of following the established procedures.
Employee Training and Awareness
Educating employees about the significance of data security and the proper use of shredders is crucial. Conduct regular training sessions on best practices for handling sensitive materials, using shredders correctly, and recognizing potential security risks. Promote a culture of security awareness and encourage employees to take responsibility for protecting sensitive information.
Information Protection Measures
In addition to shredding, incorporate other information protection measures into your security strategy. This may include implementing access controls, encryption, firewalls, and secure storage solutions. A comprehensive approach to information protection enhances overall security and minimizes the risk of data breaches.
Conclusion
Importance of Proper Security Classification
Proper security classification ensures that sensitive information is adequately protected and disposed of in a secure manner. By assigning the appropriate security classification, you can effectively safeguard personal, financial, and business data, protect against the risks of data breaches, and maintain compliance with legal and industry requirements. The careful selection of a shredder based on security classification is an essential component of a comprehensive data protection strategy.
Choosing the Right Shredder for Data Protection
When selecting a shredder, consider the specific security classification requirements of your organization. Assess the sensitivity of the data, comply with legal and industry standards, and consider factors like document capacity, security features, and maintenance needs. By choosing the right shredder and implementing proper security measures, you can ensure the efficient and secure destruction of sensitive information, contributing to overall data protection and risk mitigation.